The global lithium-ion battery market size is expected to grow by more than 12% between 2021 and 2030, while the global lead-acid battery market size is expected to grow by 5% over the same period. However, despite the rapid popularity of lithium-ion batteries in mobile and stationary devices (including boats, caravans, golf carts, and homes), several misconceptions surrounding lithium batteries persist. Whether you are choosing between different types of lithium batteries, or lead-acid and lithium batteries, it can sometimes be difficult to separate fact from fiction. To simplify the decision-making process, we have examined and debunked some of the misconceptions surrounding lithium batteries below.
“The Lithium-Based Batteries Are Too Expensive Than The Lead-Acid Batteries”

What is the cost of lithium batteries? Although lithium batteries are more expensive upfront, they have a longer life and greater usable capacity than lead-acid batteries. The average lifespan of a lithium battery is 10 times longer than that of a lead-acid battery. Over time, lithium-ion batteries will become much cheaper than lead-acid batteries. Measured in terms of cycle life, the number of times a battery can be recharged before it needs to be replaced, lithium-ion batteries can provide between 5,000 and 10,000 cycles at 80% discharge. On the other hand, flooded lead-acid and VRLA batteries can only provide 400 – 500 cycles of life at up to 80% discharge. If you cycle a lithium battery once a day, it will provide a lifetime of over 14 years, whereas standard lead-acid batteries typically last less than two years.
What is the cost of lithium batteries? Although lithium batteries are more expensive upfront, they have a longer life and greater usable capacity than lead-acid batteries. The average lifespan of a lithium battery is 10 times longer than that of a lead-acid battery. Over time, lithium-ion batteries will become much cheaper than lead-acid batteries. Measured in terms of cycle life, the number of times a battery can be recharged before it needs to be replaced, lithium-ion batteries can provide between 5,000 and 10,000 cycles at 80% discharge. On the other hand, flooded lead-acid and VRLA batteries can only provide 400 – 500 cycles of life at up to 80% discharge. If you cycle a lithium battery once a day, it will provide a lifetime of over 14 years, whereas standard lead-acid batteries typically last less than two years.
“The Lithium Batteries don’t work under cold weather”
Whether you intend to use lithium or lead-acid batteries, it is important to take low temperatures into account as they can often cause irreparable damage to certain types of batteries. For example, with standard lead-acid batteries, low temperatures can severely reduce the long-term performance and life of the battery. Temperatures below 32 degrees Fahrenheit will significantly reduce the efficiency and usable capacity of lead-acid batteries, delivering only 70% to 80% of their rated capacity at 32 degrees Fahrenheit.
Do lithium batteries work well in cold weather? Lithium-ion batteries work efficiently and lose very little capacity in cold temperatures, delivering between 95% and 98% of the battery's capacity at 32°F (32 degrees Fahrenheit). Even at 14°F, lithium batteries can deliver 80% of their rated capacity. Typically, the more lead-acid batteries you take out of a lead-acid battery at low temperatures, the worse the battery will perform. Unlike lead-acid batteries, lithium-ion batteries will start to warm up when used in cold weather, which will lower the resistance of the battery and increase the voltage, allowing your equipment to operate properly.

In addition, charging in cold weather requires a different protocol, which is crucial when you want your energy storage investment to last. Almost every type of battery – whether lead-acid or lithium – requires a more complex charging process when the temperature starts to drop. However, lead-acid batteries have a narrower range of suitable charging conditions than lithium batteries. Both lead-acid and lithium batteries need to be charged within a defined temperature range and must be charged at a lower than normal rate. For example, in cold weather, especially at temperatures below 32°F, the charging current must be reduced to 0.1°C and at temperatures below 14°F, the charging current must be reduced to 0.05°C. Failure to do so may cause irreversible damage to the battery.、
“The Lithium Batteries Are Dangerous”
You may have seen the news stories about lithium batteries catching fire in hoverboards, laptops, cars, mobile phones, and homes, but did you know that not all lithium batteries are a fire risk? Firstly, there are many different chemical types of lithium batteries:
Unlike the chemistry of lithium cobaltate batteries, lithium iron phosphate batteries generate very little heat. This is due to the very stable chemistry of LiFePO4 cells. Lithium iron phosphate batteries also have a superior chemical and mechanical structure and do not overheat to unsafe levels. This is because the charged and uncharged states of these cells are physically similar and very robust, which allows the oxygen flux of ions to remain stable during the charge cycle. In general, the oxygen and phosphorus atoms in LiFePO4 cells are tightly linked by covalent bonds, unlike the weaker cobalt-oxide bonds in cobalt-based lithium batteries such as LCO, NMC, and NCA. Therefore, when a LiFePO4 battery is overcharged or suffers physical damage, the phosphate-oxide bonds remain structurally stable, while the bonds in LiCoO2 batteries begin to break down and release excessive heat, eventually leading to thermal runaway.

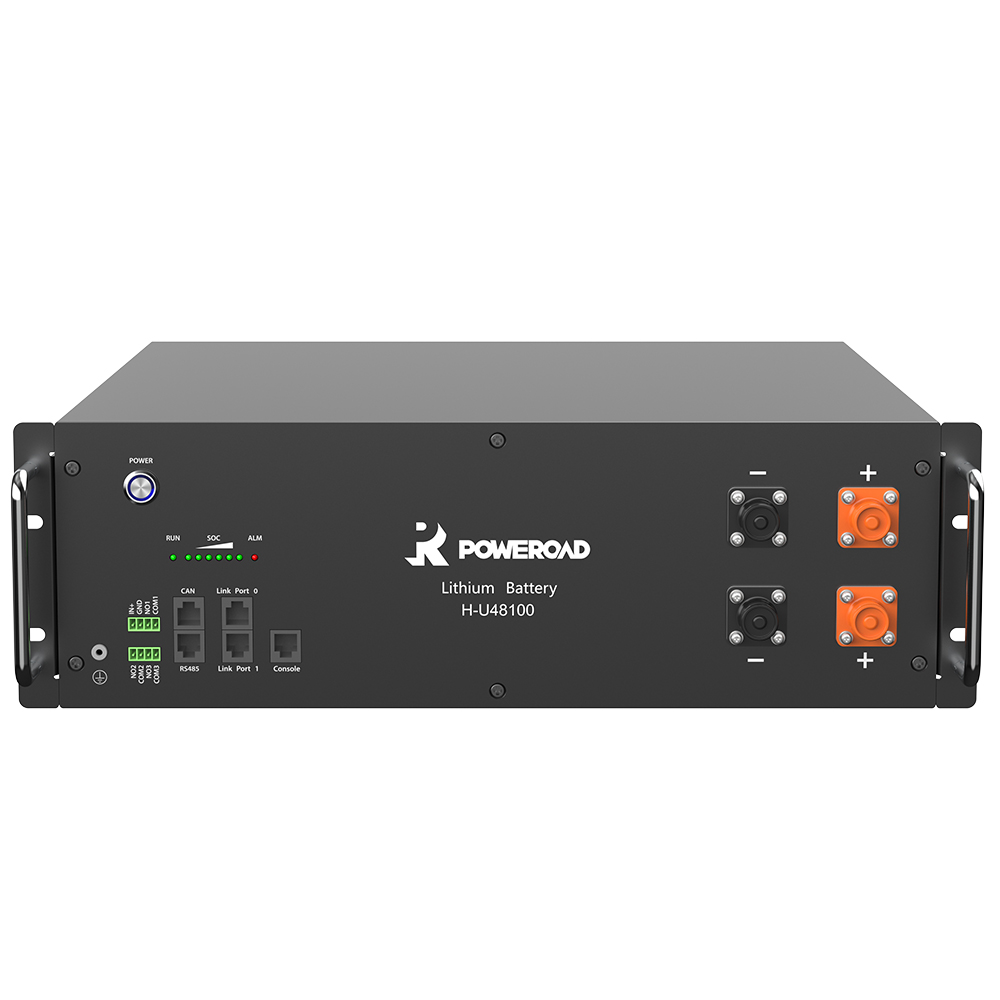
As LiFePO4 batteries are inherently safer, they also do not require additional components and therefore do not require the costs associated with cooling and thermal mitigation equipment, which is required for LiCoO2 batteries. LiFePO4 batteries are also non-flammable, can withstand harsh environments and when they are exposed to hazardous events – such as a crash or short circuit – they do not explode. LiFePO4 batteries are a safe, non-toxic, long-term solution that is worth the investment, that’s why POWEROAD insists on the LiFePO4 battery technology for over 15 years.